by Dr. William Makis, Global Research:

Papers reviewed:
- (2023 July, Seraphin et al) – The impact of vitamin D on cancer: A mini review
- (2023 June, Kuznia et al) – Efficacy of vitamin D3 supplementation on cancer mortality: Systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
- (2023 Mar, Nemeth et al) – Interplay of Vitamin D and SIRT1 in Tissue-Specific Metabolism—Potential Roles in Prevention and Treatment of Non-Communicable Diseases Including Cancer
- (2022 Oct, Henn et al) – Vitamin D in Cancer Prevention: Gaps in Current Knowledge and Room for Hope
TRUTH LIVES on at https://sgtreport.tv/

- “Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to the development and progression of a number of cancer types.”
- Vitamin D continues to show positive anti-cancer effects against many types of cancer.
- Demographic studies recommend vitamin D supplementation to prevent cancer.
- In general, the normal range for circulating 25(OH)D is 30–50 ng/mL
- deficiency is defined as < 20 ng/mL
- Breast cancer
- Vit.D deficiency common in breast cancer patients, younger and obese patients are more susceptible
- Vit.D Deficiency linked to higher grade and ER-subtypes
- Ovarian cancer – people with high Vit.D levels had 37% lower risk of ovarian cancer
- glioblastoma – induced apoptosis, cytotoxic autophagy and inhibited migration and invasiveness, and stemness
- melanoma – people on Vit.D supplements had lower risk of melanoma, low levels associated with reduced melanoma patient survival
- multiple myeloma – Vit.D treatment overcomes cancer drug resistance
- prostate cancer – Vit.D can inhibit tumor progression by negatively regulating androgen receptor signalling
- Head and neck SCC – patients with aggressive cancers had lowest Vit.D levels
- bladder cancer – Vit.D improved chemo efficacy
- osterosarcoma – Vit.D suppressed tumor growth and metastasis
- Colorectal cancer – Higher Vit.D intake resulted in 17% lower risk, suppresses colorectal cancer stem cells
- there were about 904 articles on relationship between Vitamin D and cancer during 2022-2023 (Vit.D cancer research has increased substantially)
- “low circulating vitamin D levels are associated with an increased risk of cancers”
- “supplementation alone or in combination with other chemo/immunotherapeutic drugs may improve clinical outcomes even further”
- Analysis of 14 RCTs revealed a 12 % lower cancer mortality in the vitamin D3 group compared with the placebo group in 10 trials with a daily dosing regimen (no mortality reduction was seen in 4 trials using a bolus regimen)
- Cancer survival improved when daily vitamin D3 was started before cancer diagnosis.
- Meta-analyses of observational studies reported elevated risks of lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, bladder carcinoma, and lymphoma in people with low serum 25(OH)D concentration
- Systematic reviews further concluded that sufficient 25(OH)D levels (≥50 nmol/L) are associated with better prognosis in patients with breast and colorectal cancers, whereas there have been too few studies for other cancer sites to draw conclusions
- Moreover, low 25(OH)D levels were substantially related to increased cancer mortality in the general population.
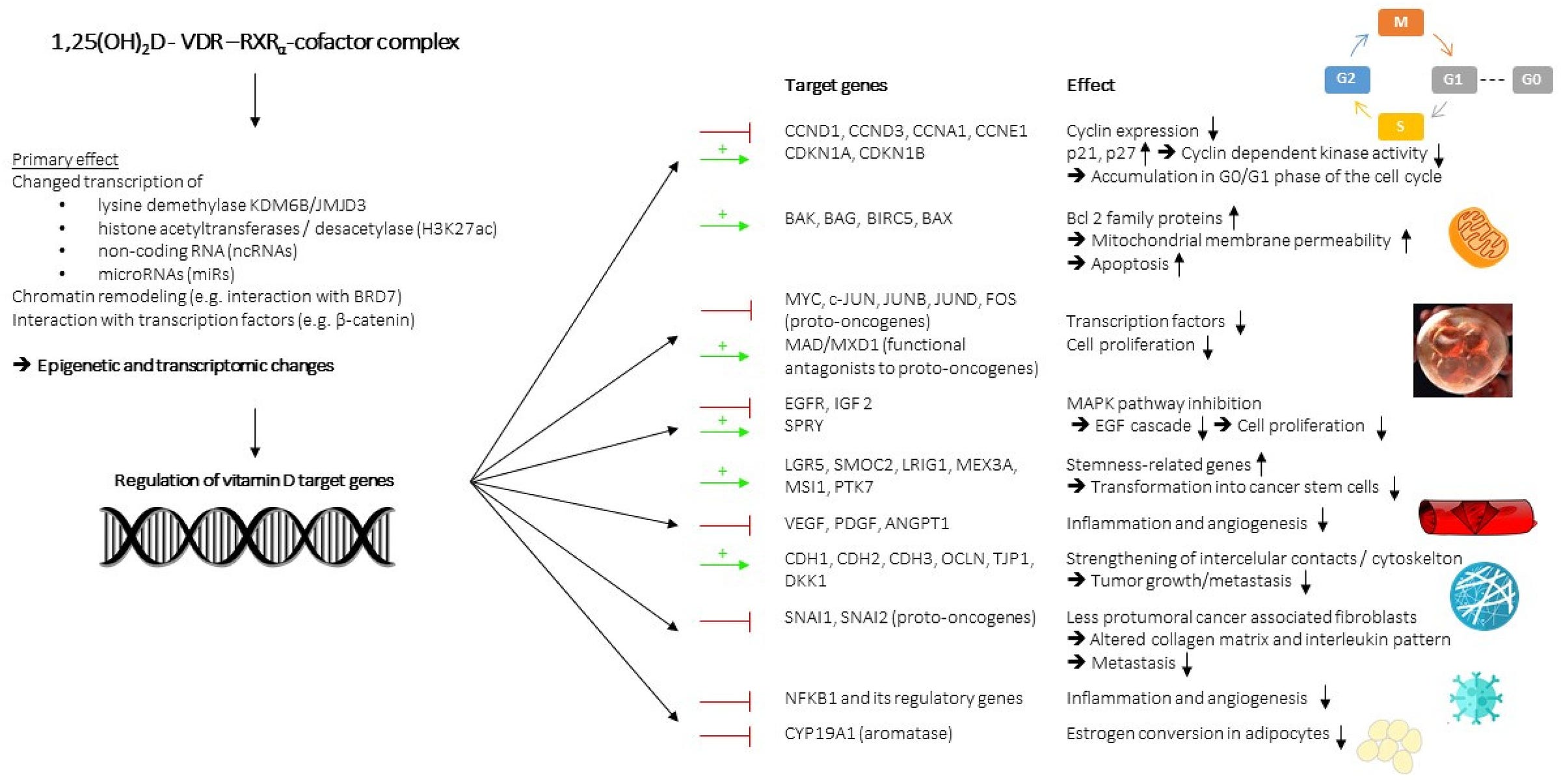
- Vitamin D decreases cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of cancer cells
- Vitamin D reduces the expression of HIF-1, VEGF, as well as IL-8, which are all important angiogenic factors (tumors need new blood vessels to grow)
- prospective and retrospective epidemiological studies reported an association between a 25(OH)D3 level below 20 ng/mL and a 30–50% increased risk of colon, prostate, and breast cancer and higher mortality
- systematic review found that vitamin D supplementation induced a shift in colon microbiome composition and increased its diversity
- “observational studies consistently showed that low vitamin D levels are associated with increased cancer incidence and mortality”
- “The potential of vitamin D for cancer prevention and add-on treatment has long been bolstered by several discovered mechanisms involving the regulation of cell growth and differentiation, apoptosis, intercellular contacts, angiogenesis, immune function, and interaction with the gut microbiome”
- “results show stronger relations between 25(OH)D and cancer mortality than cancer incidence, suggesting an impact on outcome after tumor onset. It might be explained by a gain in the relevance of 25(OH)D concentrations to counteract tumor progression to a more aggressive tumor grade, growth, and metastatic spread after initial carcinogenesis, lowering the malignancy level.”
- “The negative association between 25(OH)D plasma levels and cancer mortality is more substantial than cancer incidence. That is why vitamin D might also be considered an add-on treatment for tumor patients.”
- Vitamin D and Omega-3 Trial (VITAL) – The VITAL study investigated the effect of 2000 IU of vitamin D3 per day, combined with 1 g of marine n-3 fatty acids per day, on an invasive cancer of any type and major cardiovascular events over a median follow-up of 5.3 years.
- there was a 24% decrease in cancer incidence if your BMI was < 25
- there was a 25% decrease in cancer mortality (if you exclude first 2 years of follow-up where cancer may have existed but was undiagnosed)
- Finnish Vitamin D trial with 1600 IU/day or 3200 IU/day vs placebo in > 60 year olds showed no difference in incidence of cancer
My Take…
I’m often asked by COVID-19 mRNA Vaccinated individuals how to either prevent cancer from developing or once diagnosed, how to best treat a Turbo Cancer, given that Oncologists have no idea how to deal with this new vaccine phenomenon.
Ivermectin and Fenbendazole (or Mebendazole) have emerged as the leading options for an alternative treatment approach to mRNA Induced Turbo Cancers, however, a comprehensive treatment plan will involve several other elements.
One of these is Vitamin D.
Supplementing Vitamin D is easy and cheap.
Having high Vitamin D levels or supplementing daily with Vitamin D gives you the following potential cancer-related benefits:
- immune system support and numerous anti-cancer effects (cell cycle arrest, increased apoptosis, decreased angiogenesis, decreased cancer stem cells, decreased metastasis)
- a 10-30% decrease in the risk of getting certain cancers such as breast, ovarian, melanoma, colorectal, prostate, lung
- a 10-30% decrease in cancer mortality once diagnosed.
These are substantial benefits that cannot be ignored.



