by Dr. William Makis, Global Research:

Papers reviewed:
- 2023 Jan (Pezzani et al) – Anticancer properties of Bromelain: State-of-the-art and recent trends
- 2021 Nov (Hikisz et al) – Beneficial Properties of Bromelain
- Bromelain is an enzyme with a particular proteolytic activity that can be easily obtained from the pineapple stem (Ananas comosus)
- Bromelain’s anti-cancer properties have been evaluated extensively in dozens of studies in vitro for: breast cancer, prostate cancer, gastric, colorectal, hepatocellular, cholangiocarcinoma, lung, melanoma, lymphoma and leukemia
TRUTH LIVES on at https://sgtreport.tv/
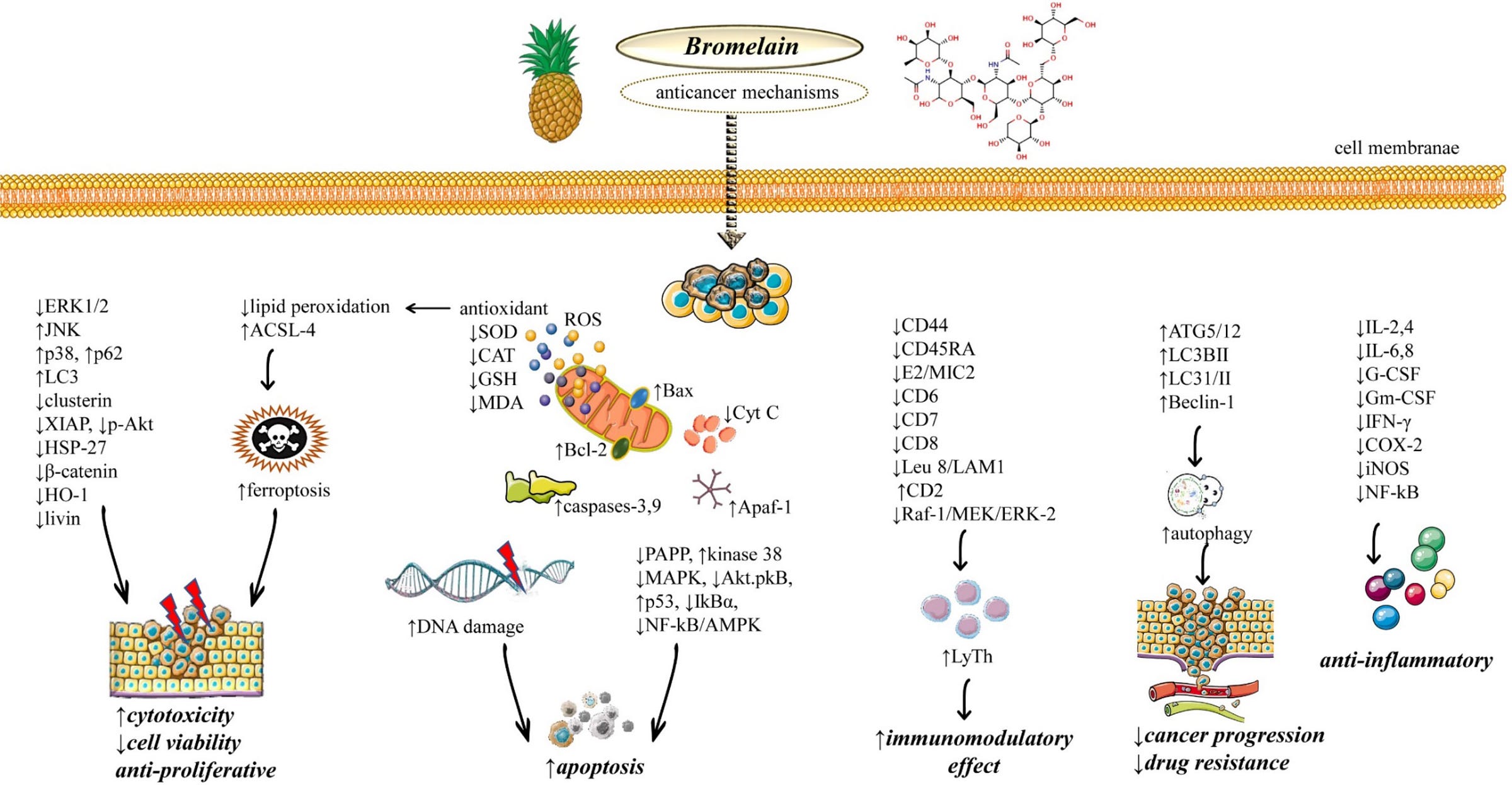
- Cytotoxicity: cytotoxic properties of bromelain known since ancient times (traditional Asian Medicine) – due to protease activity. Dose dependent.
- Apoptosis: bromelain can induce both internal and external apoptosis pathways
- autophagy: this mechanism focuses on the degradation and recycling of cellular components. Bromelain increases autophagy of cancer cells.
- Immunomodulatory: bromelain can stimulate or inhibit the immune system
- Stimulates T-cells and other immune cells and their anti-cancer activity
- anti-inflammatory: bromelain has been used since ancient times for its anti-inflammatory properties
- able to reduce inflammation and edema – bromelain reduces vasodilation, and increased capillary permeability, leukocyte migration and local pain by inhibiting the formation of bradykinin and serotonin.
- bromelain also reduces levels of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines
- Reduced cytokines/chemokines expression and alteration of white blood cell trafficking can impact on tumor microenvironment, another possible immune-mediated and anti-cancer effect of bromelain.
- Bromelain can accelerate tissue repair processes as a result of the depolymerization of intercellular structures and modification of vascular permeability (modulation of the arachidonic acid cascade)
- Combined treatment: Bromelain delivery in association with other molecules is often used to obtain a synergistic effect.
- bromelain + peroxidase: increase ROS, upregulate p53
- bromelain + olive leaf: decreased lung carcinogenesis in mice
- bromelain + curcumin + harpagophytum: reduced inflammation
- bromelain + NAC: inhibits growth and proliferation of certain mucinous tumors
- This activity can be traced back to the proteolytic activity of bromelain and the mucolytic activity of NAC
- Some tumors may use mucins during invasion, metastasis and growth in otherwise inhospitable sites
- bromelain + cisplatin: enhanced chemo effect in breast cancer
- more tumor shrinkage than cisplatin alone
- bromelain + radiation therapy: bromelain can act as a radiosensitizer and radio protector of normal tissue
- increased ROS production, inhibition of repair of DNA strand breaks and inhibition of proliferation
- bromelain has been studied as an adjuvant treatment in cancer care (not a main treatment but an addition to a main treatment)
- breast cancer patients who took bromelain for 10 days showed increased immunotoxicity effect of monocytes and lymphocytes against breast ca cells
- New drug (BromAc®) combines bromelain + NAC and is used in recurrent thoracic pseudomyxoma peritonei (PMP) treatment (mucolytic properties of BromAc® help the tumor dissolution when it was injected directly into mucinous disease)
- bromelain (in combination with papain, sodium selenite and Lens culinarislectin) has been also tested as a complementary medicine on more than 600 breast cancer patients to reduce the side effects caused by adjuvant hormone therapy.
- “Despite these promising effects, the number of clinical trials is low and limited to early stages.”
- pineapple was valued because of its pleasant, sweet taste, in addition to a wealth of nutrients such as fiber, numerous vitamins, manganese, and copper.
- studies carried out on leaf extracts of pineapple stem have shown that they also contain many biologically attractive alkaloids, flavonoids, saponins, and tannins. Currently, it is believed that the attractive healing properties of this plant can be attributed to the action of bromelain
- bromelain is an enzyme characterized by anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, immunomodulatory, antioxidant, and anticancer properties.
- Due to its low toxicity, high efficiency, high availability, and relative simplicity of acquisition, it is the object of inexhaustible interest of scientists
- bromelain is a non-toxic compound with therapeutic values, classified as a protein-digesting enzyme protease
- proteases perform many essential functions, e.g., digestion, proliferation control, cell growth and death, regulation of protein synthesis, and degradation.
- bromelain has low systemic toxicity and good absorption in the body while maintaining sufficiently high biological activity.
- safety: Animal experiments have shown that bromelain has very low toxicity with a lethal dose (LD) greater than 10 g/kg body weight.
- Immunomodulatory: Numerous studies indicate that bromelain has very complex immunomodulatory properties realized at many levels of molecular signaling pathways and control of gene expression involved in the immune response.
- bromelain may cause both an increase and a decrease in the activity/expression of the same molecules involved in the immune response
Anti-Cancer Properties
- the exact mechanism of its molecular anticancer activities is still unknown
- It has been suggested that the ability of bromelain to inhibit tumor cell proliferation and metastasis, and induce tumor cell death may be due to its proteolytic and immunomodulatory properties
- Bromelain’s ability to trigger apoptosis is undoubtedly one of its essential features allowing for effective inhibition of cancer development and proliferation
- molecular mechanisms of bromelain’s anticancer activity are carried out in many biochemical pathways



